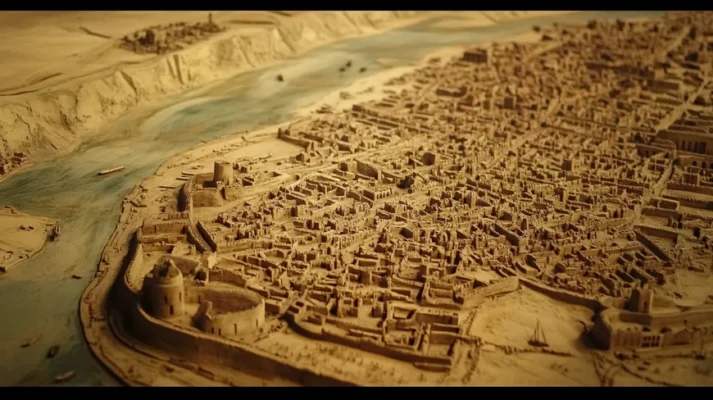
Nippur is one of the most important cities of ancient Mesopotamia, which was the center of religious and cultural life of the Sumerians. Located in modern-day Iraq, this city was founded about 5,000 years ago and became an important political, economic, and spiritual center.
Nippur gained its fame thanks to the Ekur temple, dedicated to Enlil, the supreme god of the Sumerians. The temple and the city played an important role in religious rituals that attracted pilgrims from all over Mesopotamia.
Over time, Nippur began to lose its importance, but its archaeological finds became important for the study of Sumerian civilization. Scientists have discovered numerous cuneiform tablets that provide a better understanding of the culture, religion, and administrative system of the Sumerians.
Today, Nippur is an archaeological site, and its finds are of great importance for the history of humanity, particularly in understanding the development of Mesopotamian civilizations.
History of Nippur
The history of Nippur is the history of one of the oldest and most influential cities of ancient Mesopotamia, which became an important cultural, religious, and political center of Sumerian civilization.
Foundation and heyday
Nippur was founded around the middle of the 5th millennium BC. The city was located on the Euphrates River and quickly became one of the key centers of Sumerian culture. Its strategic location and fertile lands contributed to the development of agriculture and trade relations with other cities of Mesopotamia.
Religious importance
Nippur gained its fame thanks to the Ekur temple, dedicated to the god Enlil, the patron of the city and the god of wind and thunder, who was considered one of the main deities in the Sumerian religion.
Ekur was the spiritual center of Mesopotamia, and people from other cities made pilgrimages here, hoping for the god’s blessing. Thanks to this, Nippur became not only a religious but also a political center, where important meetings and decisions for all of Mesopotamia took place.
Political significance
For centuries, Nippur was strategically important for the Sumerian city-states, as it was considered a symbol of divine authority and the legitimacy of rulers. Various rulers from other cities tried to control Nippur in order to strengthen their power and gain divine patronage.
Decline
However, after several centuries of prosperity, Nippur began to decline. This happened between 2000 and 1500 BC, when the city lost its importance due to the invasion of the Akkadians and changes in the economic and political situation. However, its cultural and religious heritage remained important for future generations.
Archaeological research
The discovery of Nippur was made possible by archaeological excavations that began in the mid-19th century. Archaeologists found numerous cuneiform tablets containing records of religious rituals, economic activities, and political events of the time.
The study of these finds provided important information about the history and culture of the Sumerians and allowed us to reconstruct the significance of Nippur in ancient times.
Thus, Nippur not only became the center of Sumerian civilization, but also left an indelible mark on human history thanks to its religious, cultural, and political influence.
The religious significance of Nippur
The religious significance of Nippur was extremely important for Sumerian civilization. The city was considered the spiritual center of Mesopotamia and played a key role in religious rituals that determined the political and social structure of society.
The Temple of Ekur and the cult of the god Enlil
The main religious site in Nippur was the huge Ekur temple, dedicated to the god Enlil, who was considered one of the most important deities in the Sumerian pantheon. Enlil was the god of wind and thunder, the patron of fertility, natural forces, and the protector of order in the cosmos. The Ekur temple, as the largest and most important religious center, became a place where religious rituals and prayers were performed, as well as where sacred texts and records were kept.
The religious role of Nippur for all Sumerian cities
Nippur was not the capital of any of the Sumerian city-states, but it had enormous religious significance.
The city was considered sacred and was believed to be a place where the gods communicated directly with humans. For this reason, Nippur was often the object of worship and pilgrimage from other parts of Mesopotamia. The rulers of the Sumerian cities came to Nippur to receive divine blessings to legitimize their power and strengthen their position.
Sacred rituals and sacrifices
Religious rituals in Nippur, which were performed in the temple of Ekur, included sacrifices, prayers, and purification rituals. Important holidays were various rituals dedicated to the god Enlil, which took place on holy days. These rituals not only maintained the spiritual connection between people and gods, but also gave the peaceful inhabitants a sense of well-being and harmony in the world around them.
Significance for cultural heritage
Nippur was not only a religious center, but also a place where sacred records were kept. One of the important aspects of religious life in Nippur was the numerous cuneiform tablets containing religious texts, myths, prayers, and instructions for performing rituals. These records became the basis for understanding the religious practices of the Sumerians and were an important source for studying Sumerian mythology and religion.
Influence on subsequent cultures
The influence of Nippur’s religious life was not limited to the Sumerians. After the decline of Nippur, its religious traditions and the cult of Enlil were adopted by other cultures of Mesopotamia, notably the Akkadians, and later the Babylonians and Assyrians.
Thus, Nippur was not only an important religious center for the Sumerians, but also had a great influence on the development of religion and culture in Mesopotamia, leaving a legacy that continued to influence civilizations in the region for many centuries.
Archaeological finds
Archaeological finds in Nippur are of great importance for the study of ancient Sumerian civilization, as they allow us to reconstruct the religious, social, and economic life of the city. During excavations, numerous artifacts were found that give an insight into the culture, art, and everyday life of the Sumerians.
Cuneiform tablets
One of the most valuable archaeological finds are numerous cuneiform tablets containing texts about religious rituals, laws, administrative records, and economic agreements. They are important sources for studying the political and social organization of Nippur. These tablets also contain myths and epics that provide insight into the religious beliefs and customs of the Sumerians.
Ekur Temple
One of the greatest archaeological finds is the remains of the Ekur Temple, which was dedicated to the god Enlil. The temple was of great importance to the religious life of Nippur, and its ruins reveal the richness of the architecture and art of the time. Archaeologists have found fragments of statues, carved stones, and other cult objects that testify to the high level of craftsmanship and religious art of the Sumerians.
Household artifacts and cult objects
The excavations also uncovered numerous household artifacts: pottery, tools, jewelry, and objects used in everyday life. Cult objects such as small statues of deities, amulets, and religious symbols are also important. These items provide insight into the beliefs and religious practices of the people of Nippur.
Graves and tombs
The graves and tombs discovered by archaeologists have helped to determine how the inhabitants of Nippur were buried and what they considered important in death. Some tombs contained items that belonged to the deceased, allowing conclusions to be drawn about the social status and cultural characteristics of the burial.
Architectural remains
Excavations in Nippur also allow us to study the remains of the city’s architectural structures. These include walls, gates, and buildings that testify to the city’s developed infrastructure. The remains of the city walls help to determine the scale and defensive strength of Nippur, as well as its layout as an important urban center.
Mythological texts and literary works
In addition to administrative and religious texts, archaeologists have also found records of literary works such as myths, epics, and stories describing the exploits of gods and heroes. These texts not only preserve the mythological beliefs of the Sumerians, but are also an important source for studying their cultural values and traditions.
Impact on the understanding of Sumerian culture
Archaeological finds in Nippur allow researchers to reconstruct important aspects of Sumerian culture, including their religious beliefs, social organization, and level of technological development. The finds also help in studying the relationships between different cities in Mesopotamia and provide important information for reconstructing the history of the Ancient Near East.
Thus, the archaeological excavations at Nippur have become an important tool for reconstructing the ancient world and studying the life of one of the oldest civilizations.
Consequences for history and culture
As one of the largest and most important cities of ancient Mesopotamia, Nippur had a significant influence on the development of history, culture, and religion not only of the Sumerians but of the entire Near East. The consequences of this city for the civilizations of subsequent stages were profound and multifaceted.
Religious heritage
Nippur, thanks to the temple of Ekur and the cult of the god Enlil, became a spiritual center for the Sumerians, Akkadians, Babylonians, and Assyrians. The religious practices that originated in Nippur influenced the religious beliefs of other peoples of Mesopotamia. The god Enlil, patron of Nippur, became an important deity for the entire region, and his cult spread to other civilizations. The city also became a symbol of the divine legitimacy of rulers: no ruler of Mesopotamia could be considered a true ruler without receiving divine blessing, which he sought in Nippur.
Cultural heritage
The finds in Nippur, in particular literary texts and cuneiform tablets, became the basis for the study of Sumerian literature and mythology. The myths, epics, religious hymns, and laws recorded on the tablets not only reflect the cultural and spiritual ideas of the Sumerians but also influenced later literary traditions. They also became the basis for the development of writing in other cultures of Mesopotamia and even beyond.
Political influence
Nippur was crucial for the political legitimacy of rulers. It was believed that only a ruler who had received divine blessing in Nippur had the right to rule. This city became a symbol of cosmic order, where earthly rulers had to confirm their power through religious rituals. This aspect of political organization spread to other cultures, including the Akkadians, Babylonians, and Assyrians, creating common political and religious traditions within Mesopotamia.
Contribution to the development of writing
Nippur became the center of the development of cuneiform writing. Archaeologists have found a large number of tablets containing administrative records as well as religious and cultural texts. The study of these tablets has helped to decipher cuneiform writing and understand the development of writing in the ancient world. In addition, the large number of these texts preserved in the archives of Nippur provide unique evidence of the daily life, economic activities, religious beliefs, and cultural traditions of that time.
Architectural and technological development
Nippur was an important center not only for religious but also for technological development. Architectural remains, in particular the temple of Ekur, testify to the high level of construction technology at that time.
The development of crafts such as pottery, metalworking, and textile manufacturing is also reflected in the archaeological finds of Nippur. The technologies developed in Nippur later influenced other cities in Mesopotamia, as well as the development of civilizations in the Mediterranean.
Intercultural influence
As an important cultural and religious center, Nippur facilitated the exchange of ideas and technologies between different cultures in Mesopotamia, which had a huge impact on the development of civilizations in the region.
The city became a place of cultural exchange between the Sumerians, Akkadians, Amorites, Babylonians, and Assyrians, which contributed to the development of common traditions, religious beliefs, and administrative practices.
Due to its role as a religious, cultural, and political center, Nippur had a major influence on the formation of the ancient civilizations of Mesopotamia. Its legacy has not only been preserved in archaeological finds, but has also become the basis for the development of religious and cultural traditions that have had a profound influence on subsequent generations and civilizations in the region.
Conclusions
Nippur played an extremely important role in the development of the ancient civilizations of Mesopotamia, and its influence extended far beyond the Sumerian culture. The city became not only a religious and cultural center, but also an important political center where the foundations for the organization of society and government were laid.
The Temple of Ekur, dedicated to the god Enlil, became a symbol of the divine legitimacy of the rulers, and the religious rituals of Nippur had a profound influence on the cultures of other peoples of Mesopotamia.
Archaeological finds, such as cuneiform tablets, cultural artifacts, and architectural remains, provide important information for reconstructing the life of that time and the development of writing. The finds in Nippur allow modern scholars to study the religious, social, and political aspects of Sumerian civilization, as well as to reconstruct cultural traditions that were formed over centuries.
Thus, Nippur was not only an important city for the Sumerians, but also became a symbol of cultural and religious heritage that greatly influenced the development of subsequent civilizations. Its influence can be traced in architectural, literary, religious, and political traditions that have left a deep mark on human history.