Nefertiti was the wife of Pharaoh Akhenaten, who ruled Egypt in the 14th century BC. Her name means “Beautiful Appearance.” This woman played an important role in her husband’s life and in the history of Ancient Egypt as a whole.
Nefertiti was born around 1370 BC and was the daughter of the influential nobleman Ay. At the age of 15, she became the wife of Akhenaten, who was then a prince. After Akhenaten became pharaoh, Nefertiti became co-ruler.
Nefertiti was known for her beauty and grace, as well as her rare political skills. She held an important position in the government and administration of state affairs, and is also known for her support of the new religion introduced by her husband. Nefertiti was also known for promoting the arts and culture at a time when the country was undergoing great change.
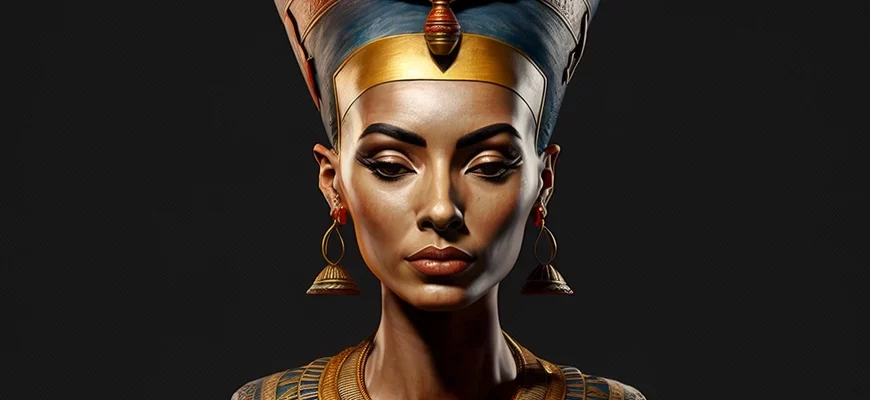
In art, Nefertiti is known for her image. Her portrait, found in a cave in 1912, is one of the most famous works of art from Ancient Egypt. Her image is rendered with great precision and realism and has become a model for many other artists.
Nefertiti was also known for her support of the new religion. Her husband Akhenaten attempted to introduce a monotheistic religion, rejecting the traditional pantheon of gods
However, this attempt did not find widespread acceptance in the country, and after Akhenaten’s death, the traditional religion was restored. Nevertheless, Nefertiti remained faithful to her idea of monotheism, and this may have been one of the reasons for her loss of popularity among subsequent pharaohs.
Nefertiti was also known for her contribution to politics and the management of state affairs. She held an important position in the government and promoted reforms aimed at strengthening the pharaoh’s power and the political stability of the country.
Despite her great contribution to the development of Ancient Egypt, much of Nefertiti’s life remains a mystery. For example, it is not known when she died or where she is buried. Some scholars believe that Nefertiti may be buried in an unknown location in the Amarna Valley, where she lived with her husband and family.
In any case, Nefertiti remains one of the most prominent and mysterious figures in the history of Ancient Egypt, and her contribution to the culture, art, and politics of the country remains unforgettable.
Early life and marriage to Pharaoh Akhenaten
Nefertiti’s early life remains a mystery, as very little is known about her before she became the wife of Pharaoh Akhenaten. She was born around 1370 BC in the city of Akhetaten (now Tel el-Amarna) into the family of a high-ranking official who had connections to the royal court.
In 1353 BC, Nefertiti married the young Pharaoh Akhenaten when she was about 15 years old. Akhenaten was one of the most controversial pharaohs in the history of Ancient Egypt, as he was the first pharaoh to introduce monotheism—the cult of the sun god Aten—excluding other gods from the faith.
After the wedding, Nefertiti was Akhenaten’s leading wife, and she received the honorary title of “Chief Wife of the Pharaoh.” This meant that she was the most important woman in Egypt after the pharaoh himself. She was also known for her beauty and elegance, which was reflected in her portraits found in Amarna and other places.
During her marriage to Akhenaten, Nefertiti gave birth to six daughters but no sons, which was a major problem for the dynasty. The lack of an heir caused political and social instability, as it was necessary to find an heir who would ensure the continuation of the dynasty. As a result, some scholars believe that Nefertiti may have been the mother of Tutankhamun, who became the next pharaoh after Akhenaten’s death.
Nefertiti was not only Akhenaten’s wife, but also an influential political figure in the state. She played an important role in introducing the cult of Aten and reforming religion. She also pursued her own foreign policy, conducting diplomatic negotiations with other states and signing treaties.
Nefertiti’s contribution to history lies in the fact that she played an important role in the transition period between the Old and Late Kingdoms of Egypt. She contributed to the flourishing of culture and art, and also helped to develop the state’s trade and economy. In addition, her influence on Egyptian politics and religion was later reflected in the country’s history and culture.
Nefertiti’s death and legacy remain a mystery. There are some theories that she died early, possibly from illness or after childbirth. Other scholars believe that she was simply forgotten after the death of Akhenaten and other important members of his family.
In any case, Nefertiti left her mark on Egyptian history, which will be remembered for her contribution to the development of culture, art, and religion.
Cultural contribution and influence on art
Nefertiti was known not only as an influential political figure, but also as a patron of art and culture. She made a significant contribution to the development of art and architecture in Egypt.
One of the most famous examples of art associated with Nefertiti is her bust, discovered in 1912 in the city of Amarna. This bust has become one of the most significant artifacts of Egyptian art. The bust of Nefertiti depicts her with a clearly defined symmetrical face and a high chin, which became the hallmark of the art of the Akhenaten era.
In addition, Nefertiti is also known for her support of art and architecture. She commissioned many construction projects, including temples and palaces. For example, she helped build the huge Temple of Aten in Amarna, which became one of the largest and most significant temples in Egypt.
Nefertiti also supported the development of music and dance in Egypt. Her role as a patron of the arts and culture contributed to the development of many other art forms, such as literature, poetry, and others.
Nefertiti’s influence on Egyptian art was significant. She contributed to the development of new technologies and styles in art, which became known as the “Amarna style.” This style, characteristic of the era of Akhenaten and Nefertiti, was different from traditional Egyptian art and architecture, as it reflected new views on religion, art, and architecture. The Amarna style is characterized by very realistic depictions of human faces and figures, which differed from standard Egyptian forms and were more naturalistic.
In addition, Nefertiti also made a significant contribution to the development of Egyptian culture and religion. She supported the cult of Aten and promoted the development of a monotheistic cult in which Aten was the only deity. This became a new religious concept that replaced the traditional polytheism that was characteristic of Egyptian religion.
Nefertiti also influenced the role of women in Egyptian society. She was depicted in many different poses that showed her as an influential and powerful figure. This differed from the standard depictions of women in Egyptian art, who were usually shown in a subordinate position next to their husbands.
Ultimately, Nefertiti was one of the most famous and influential women in Egyptian history. Her contribution to the development of art, architecture, culture, and religion in Egypt was significant and influential, and she left an indelible mark on the history of the country.
The mysteries of her mysterious disappearance
The Egyptian queen Nefertiti is one of the most mysterious figures in Egyptian history. Her sudden disappearance from Egyptian history remains an unknown and debated issue among historians and archaeologists.
There are several versions of what happened to Nefertiti. One of them claims that she died around the same time as her husband, Pharaoh Akhenaten. Another version claims that she fled the palace and went into exile.
There is also a hypothesis that Nefertiti was reincarnated into another person, namely the Egyptian queen Mortal It. This theory is based on images showing Mortal It with a face very similar to that of Nefertiti.
Another version says that Nefertiti fell victim to intrigue and was killed or murdered for trying to preserve her status and power.
Regardless of what happened to Nefertiti, her fame and influence on the history of Egypt remain alive to this day.
Her role in the development of Egyptian art, architecture, and religion remains undeniable, and her name will forever be associated with the history of this country.
The queen’s legacy and heirs
After the death of the Egyptian queen Nefertiti, her legacy passed to her children and the subsequent rulers of Egypt. Unfortunately, the fates of many of Nefertiti’s children remain unknown.
However, some of Nefertiti’s children are mentioned in Egyptian history. The most famous of these are her two daughters, Meritaten and Ankhesenamun, as well as her son, Tutankhamun.
Meritaten was the eldest daughter of Nefertiti and Pharaoh Akhenaten. She had a great influence on the politics and religion of Egypt during her reign as pharaoh. Ankhesenamun was the younger daughter of Nefertiti and Akhenaten, and she also had a significant influence on the religion and culture of Egypt.
Tutankhamun, the son of Nefertiti and another pharaoh, was known for restoring traditional religion and culture after the reign of his father and older brother. His fame increased with the discovery of his necropolis in 1922, where his treasures and burial were found.
Although the fate of most of Nefertiti’s children remains unknown, her influence on Egyptian history and culture has transcended time and remains undeniable.