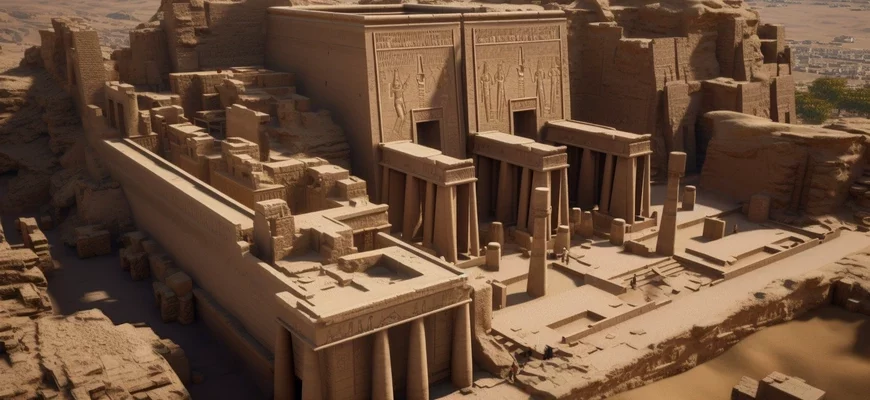
Ancient Egyptian temples were magnificent structures built for worship and prayer. Their architecture was impressive in its complexity and detail. Temples were of great religious significance, as they were believed to be the dwelling places of the gods. The most famous of these are the temples at Karnak, Luxor, and Abu Simbel. They are examples of exquisite architecture and are of great cultural and historical value.
Temple architecture
The architecture of ancient Egyptian temples was complex and detailed. The temples consisted of many structures, including sanctuaries, chapels, colonnades, and stairways. One of the most striking elements of the architecture was the large columns that adorned the entrance gates and worship halls. Another characteristic element was the intricate reliefs depicting the gods and their stories. Building materials such as granite, sandstone, and stone clay were used to create monumental structures. The architecture of ancient Egyptian temples is of great cultural and historical value and continues to impress with its sophistication and beauty to this day.
Types of temples
There were many different types of temples in ancient Egypt. One of the most famous is the osiris temple, consisting of several stone blocks connected with metal brackets. Another type is the temple complex, which consists of several temples connected by common courtyards and gates. A chapel temple consists of a sanctuary where a divine image is kept and a hall intended for worship. A fortress temple was used as a defensive structure, and a colossal temple, whose image consisted of large statues, served for worship and honoring the gods. Each of these types of temples had its own unique features and purpose, making them important historical and cultural monuments.
Temple design
The design of ancient Egyptian temples was carried out with great attention to detail and symbolism. One of the most famous design elements is the large columns with reliefs that adorned the entrance gates and worship halls. The temples also featured intricate paintings depicting the gods and their stories, as well as majestic sculptures reflecting divinity and power. The design of the temples had symbolic meaning and served to reflect religious and cultural ideals. The uniqueness and beauty of the design of the temples of ancient Egypt make them one of the most fascinating and impressive monuments in the world.
Religious significance of temples
The temples of ancient Egypt had a deep religious significance for the population of this country. They were used to perform various religious rituals and services intended to honor gods and goddesses. Temples were also places where sacred images, amulets, and other religious artifacts were kept. Some temples contained shrines that were considered sacred and were accessible only to highly initiated individuals. In addition, temples served as centers of social life, where people gathered to discuss religious and cultural issues, trade, and receive education. All this testifies to the importance of temples in the life of the ancient Egyptians and the significance of religion in the history and culture of this country.
Examples of famous temples
Ancient Egypt is famous for its impressive temples, many of which have survived to this day and are popular tourist attractions. One of the most famous temples in Egypt is the Karnak Temple in Luxor, which was built about 4,000 years ago. The temple consists of several terraces and halls containing numerous statues and reliefs depicting religious and historical events.
Another notable temple is the Temple of Hatshepsut, located in the Valley of the Kings near Luxor. This temple was built in honor of Pharaoh Hatshepsut and is decorated with impressive reliefs depicting the pharaoh’s travels to distant countries.
Other famous temples in Egypt include the Temple of Isis in Philae, the Temple of Abu Simbel, and the Temple of Hor-Habu. Each of these temples has its own unique history and architectural style, making them unforgettable experiences for anyone who has the opportunity to visit them.
Karnak Temple
Karnak Temple is one of the largest and most impressive temples of Ancient Egypt, located east of the Nile River in the city of Luxor. It was founded around 2000 BC and expanded over many centuries.
The Karnak Temple consists of numerous structures, including the Temple of Amun, the Temple of Mut, and the Temple of Montu. Each of these temples has its own history and architectural features.
One of the most impressive elements of Karnak Temple is the “Alley of Sphinxes,” which contains more than 1,300 statues of sphinxes with the heads of gods and the bodies of lions. Other notable architectural features of the temple include the “Colonnade of the Pharaohs,” consisting of 134 columns, and the “Sanctuary of Sanctuaries,” which is the sacred place where the sacred image of the god Amun was placed.
The Karnak Temple is an outstanding example of ancient Egyptian architecture and art and served as an important center of religious and cultural life in Ancient Egypt. Today, it remains one of the most famous tourist destinations in Egypt.
Luxor Temple
Luxor Temple, or Temple of Amun in Luxor, is one of the greatest temples of ancient Egypt. It is located east of the Nile River in the city of Luxor, on the site of the center of the cult of Amun, one of the most important gods of ancient Egyptian religion.
Luxor Temple was founded more than 3,000 years ago, during the New Kingdom, and has been under constant construction and reconstruction for many centuries. It consists of numerous structures, including the Temple of Amun, the Temple of Mut, and the Temple of Montu.
One of the most famous elements of the Luxor Temple is the “Hall of Columns,” which consists of 32 large columns, each over 20 meters high and decorated with detailed reliefs. Other impressive elements of the temple include the “Ramses III Enclosure,” where several statues of the pharaoh have been preserved, and the “Temple of Hatshepsut,” which was built in honor of one of the most famous pharaohs.
The Luxor Temple is considered an important example of ancient Egyptian architecture and art and is one of the most visited tourist sites in Egypt. It is also an important source of information about the religious and cultural life of ancient Egyptian civilization.
Abu Simbel Temple
The Abu Simbel Temple is one of the most famous and impressive monuments of ancient Egypt. It is located in southwestern Egypt, on the banks of the Nile River, near the modern city of Aswan.
The temple was built by Pharaoh Ramses II around 1279-1213 BC and decorated with huge statues of the pharaoh, over 20 meters high, and his wife Nefertari. These statues, considered among the tallest monuments of ancient Egypt, are famous symbols of pharaonic power and grandeur.
The temple consists of two main structures – the Great Temple and the Small Temple. The Great Temple consists of two halls decorated with reliefs depicting the life and achievements of Ramses II. The Small Temple is dedicated to Ramses II’s wife, Nefertari, and contains many reliefs depicting her life and religious rituals.
In the 1960s, the temple was dismantled and moved to higher ground to save it from flooding caused by the construction of a hydroelectric power station on the Nile River. It was one of the largest and most complex restoration projects in the history of world archaeology.
The Abu Simbel Temple is considered a tremendous achievement of ancient Egyptian architecture and art. It is a popular tourist destination and one of the most visited monuments in Egypt.