The Sumerians were one of the world’s oldest civilizations, flourishing in Mesopotamia between the 4th and 3rd millennia BC. Their scientific achievements include significant contributions to mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and culture.
The Sumerians created a number system based on the number 60, which served as the basis for the modern system of measuring time and angles. They also studied geometry and algebra, advanced in the field of astronomy by observing stars and planets, and created the first calendar.
In medicine, the Sumerians made significant discoveries in the field of surgery and medical inventions. In culture and art, the Sumerians developed writing on clay tablets and were also involved in architecture, sculpture, and painting.
The scientific achievements of the Sumerians had a significant impact on the development of science and culture in subsequent centuries, and their discoveries are still used in the modern world.
Mathematics
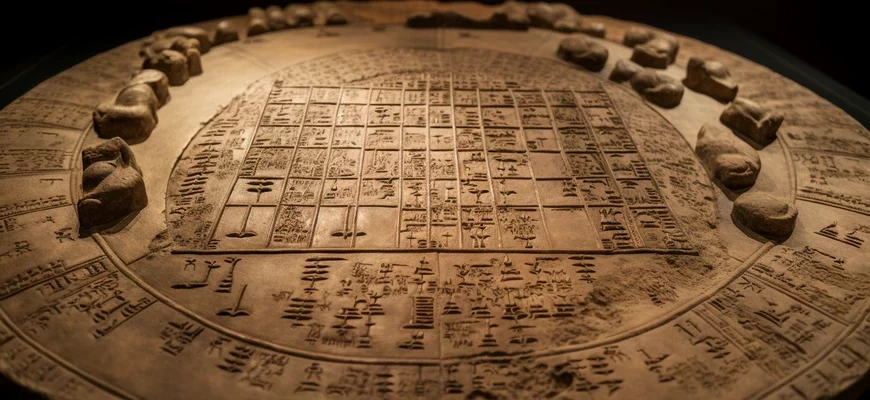
The Sumerian civilization (c. 4000-2000 BC) was one of the first in human history to develop mathematics and perform calculations. Sumerian mathematics was basic but very practical. The Sumerians used a number system of 60, called the sexagesimal system, which became the basis for further mathematical developments in history.
Sumerian mathematicians solved problems related to trade, agriculture, and construction. They studied geometry to measure land and construct buildings, and they studied arithmetic to calculate trade transactions and time.
The Sumerians created multiplication and division tables in which problems with fractions were solved. Methods were also developed to calculate the area of triangles, circles, and other shapes.
One of the most famous inventions of Sumerian mathematicians was the introduction of the concept of zero. They used an empty space to indicate the absence of something, which allowed them to perform more complex calculations and use more accurate methods.
Astronomy
The ancient Sumerians were known for their knowledge of astronomy. They believed that stars and planets had a great influence on life on Earth and used their knowledge to develop calendars, predict the weather, and forecast events.
To study celestial bodies, the ancient Sumerians created special instruments such as astrolabes and gnomons. They also used observations to determine the time of year, the lunar cycle, and other celestial events.
The ancient Sumerians used a number system based on 60, which allowed them to develop an accurate calendar consisting of 12 months of 30 days each. Each month was given a name associated with celestial objects such as the Sun and Moon.
Creation of the calendar
The ancient Sumerians were one of the first peoples to develop a calendar system. They created a calendar based on the cycle of full moons, or the so-called lunar calendar. The calendar consisted of 12 months, each lasting from the beginning of the new moon to the beginning of the next. Each month consisted of 29 or 30 days, depending on the phase of the moon.
However, since the month lasts about 29.5 days, the lunar calendar differed from the solar calendar by half a day per year. Therefore, the ancient Sumerians added an extra month called “Shulgi” every five years to help align the lunar calendar with the solar calendar. This allowed them to more accurately determine the seasons and make predictions for agriculture.
In addition, the ancient Sumerians also observed the movement of celestial bodies and created astronomical tables containing detailed information about the positions of the planets, the sun, and the moon. These tables allowed them to predict solar and lunar eclipses, as well as predict the movement of planets in the sky. The ancient Sumerians were also the first to use planets instead of stars to determine time and move from one place to another.
Medicine
Medicine was a very important field for the ancient Sumerians, who developed many methods of treatment and used various means to treat different diseases.
Sumerian doctors had extensive knowledge of the anatomy of the human body and the ability to diagnose various diseases. They studied the symptoms of diseases and conducted research to develop treatment methods. Doctors used various treatment methods, such as massage, bloodletting, and the use of various potions and other medicinal preparations.
The ancient Sumerians believed that many diseases were caused by the wrath of the gods, so doctors used religious rituals and ceremonies to treat the sick. For example, they might ask a god to rid the patient of their illness.
The development of surgery
The ancient Sumerians made a great contribution to the development of surgery. They were the first to use instruments for surgical operations and apply anesthetics to reduce pain during operations.
One of the most famous Sumerian surgeons was Imhotep, who lived in the third millennium BC. He is credited with inventions in the field of surgery, including the use of sharp knives for operations and the use of painkillers.
The ancient Sumerians also knew about bacteria and infections and used antiseptics to prevent wound infections. They used various plants and herbs that had antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties to reduce the risk of infection and speed up wound healing.
In addition, the ancient Sumerians were the first to describe treatments for certain diseases, such as coughs, headaches, and acute hepatitis. They also used honey to treat various diseases and reduce inflammation.
Overall, the ancient Sumerians were a very advanced people in the field of medicine and surgery, and their achievements in this area influenced the development of medicine in subsequent centuries.
Culture and art
The Sumerian civilization was one of the oldest civilizations in the world, existing in the region between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers in the Persian Gulf basin in the 3rd-2nd millennia BC. The culture and art of the ancient Sumerians were highly developed and diverse.
Sumerian art included sculpture, graphics, wall paintings, and other types of visual art. They used relatively simple materials such as clay, stone, and copper to create a variety of sculptures and figurines. Their works were impressive in their detail and sophistication.
One of the most famous examples of Sumerian sculpture is the “Mystery” statues – heads with a bow around the head, which were considered a kind of symbol of Sumerian art. Another important branch of art was graphics and wall paintings, which depicted scenes from everyday life, gods, and historical events.
Sumerian culture was also rich in literature. The most famous works are the epics “Gilgamesh,” “Enuma Elish,” and “Songs of Sumer and Akkad,” which were written on clay writing tablets.
Architecture
The architecture of the ancient Sumerians was quite advanced for its time. Sumerian cities were surrounded by huge walls made of clay, stone, and rich decorative ceramics. Buildings were usually made of clay, but stone blocks were used for palaces and temples.
One of the most famous structures of the ancient Sumerians were buildings used to store food supplies and other valuables. These buildings consisted of several floors that could be reached by stairs. Buildings for religious purposes, such as temples, were also constructed, mostly made of stone.
Another important building in Sumerian architecture was the palace, which served as the residence of the rulers and their families. These buildings were usually large and consisted of several rooms, such as a reception hall, bedrooms, and meeting rooms.
In order to make the buildings sturdy, the Sumerians used clay bonding technology and stone foundations and pillars. They were also known for their ability to provide sewage and water supply, using water from rivers and canals to supply water to buildings and irrigate agricultural land.
Overall, the architecture of the ancient Sumerians was very inventive and advanced for its time, suggesting that they were one of the first peoples to design and construct complex buildings and infrastructure. They played an important role in creating cultural and economic centers where trade, crafts, and other areas of life flourished.
Sculpture and painting
Sculpture and painting were an important part of ancient Sumerian culture. Their works had religious and cultural significance and were linked to the beliefs and traditions of the Sumerian people.
Sumerian sculpture was usually made of clay, wood, or stone. The sculptures depicted people, deities, animals, and various symbols. Most sculptures depicted people or deities, usually in life size or slightly larger. The sculptures were detailed and realistic, with clear facial features and clothing.
Sumerian paintings were usually made on the walls of temples and palaces. They were images of gods, signs, and symbols that reflected the religious beliefs and stories of the Sumerian people. The paintings were done in bright colors and were extremely detailed. Sumerian artists skillfully used perspective and proportion to create the illusion of depth and movement.
Sumerian paintings and sculptures were not only works of art, but also an important part of the religious and cultural life of the ancient Sumerians. They reflected their beliefs and traditions, as well as the history and life of this ancient people.
Conclusions
The ancient Sumerians made significant scientific achievements in various fields that influenced the development of human civilization. Some of these achievements include:
Invention of writing: Sumerian writing was one of the first in the world and had a huge impact on the development of culture and science. Sumerian writing was done on clay tablets and included many different symbols, allowing them to write about anything imaginable.
Astronomical observations: The Sumerians were among the first peoples to study astronomy and make systematic observations of the movement of stars and planets. They created the first astronomical calendar, which consisted of 12 months of 30 days each.
Mathematical achievements: The Sumerians used the decimal system and developed mathematics, which allowed them to perform complex calculations and solve mathematical problems.
Architecture: The Sumerians were pioneers in the construction of large cities, including Ur and Nippur, which had impressive structures such as temples, palaces, and fortresses.
Medicine: The Sumerians used plants and herbs to treat various diseases, performed complex operations, and treated wounds.
These achievements testify to the high level of development of Sumerian civilization and its influence on the further development of science, culture, and technology.